介绍 Span 的嵌套、传播、链接关系
Span 嵌套
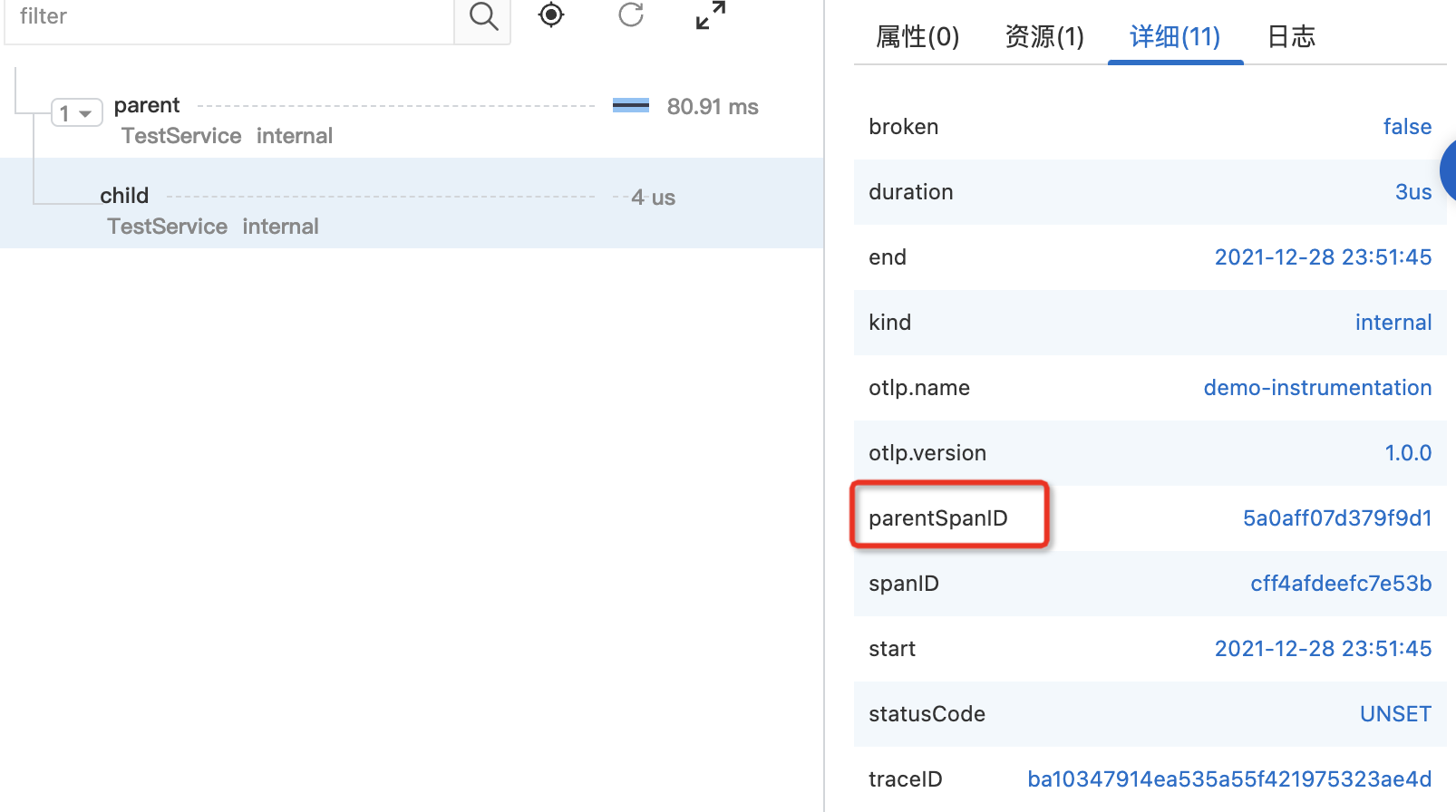
通过 setParent 方法 Span 的上下文环境
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| void parentOne() {
Span parentSpan = tracer.spanBuilder("parent").startSpan();
try {
childOne(parentSpan);
} finally {
parentSpan.end();
}
}
void childOne(Span parentSpan) {
Span childSpan = tracer.spanBuilder("child")
.setParent(Context.current().with(parentSpan))
.startSpan();
try {
} finally {
childSpan.end();
}
}
|
Span 传播(propagate)
通过调用 makeCurrent 方法,将 Span 传播为当前上下文
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| void parentTwo() {
Span parentSpan = tracer.spanBuilder("parent").startSpan();
try(Scope scope = parentSpan.makeCurrent()) {
childTwo();
} finally {
parentSpan.end();
}
}
void childTwo() {
Span childSpan = tracer.spanBuilder("child")
.startSpan();
try(Scope scope = childSpan.makeCurrent()) {
} finally {
childSpan.end();
}
}
|
获取当前 Span
1
2
3
4
5
|
Span span = Span.current();
Span span = Span.fromContext(context);
|
Span 链接(SpanLink)
用于表示 Span 之间的关联关系,如下代码,两个 span 存在关联关系,但不是嵌套关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| void parentOne() {
Span parentSpan = tracer.spanBuilder("parent").startSpan();
try {
childOne(parentSpan);
} finally {
parentSpan.end();
}
}
void childOne(Span parentSpan) {
Span testSpan=tracer.spanBuilder("test").startSpan();
Span childSpan = tracer.spanBuilder("child")
.addLink(parentSpan.getSpanContext())
.addLink(testSpan.getSpanContext())
.startSpan();
testSpan.end();
try {
} finally {
childSpan.end();
}
}
|
