运行机制 分隔符制导翻译获取输入后,通过某种分隔字符将输入分解为小块。
行符分类 行结束符 使用反斜杠表示一行的最后一个字符。
如下,逐行读取,以换行分隔符\n结束
1 2 3 score 300 for 3 nights at Bree score 200 for 2 nights at Dol Amroth score 150 for 2 nights at Orthanc
续行符 如果一行的最后一个非空白符,就表示下一行还是同一行。
行自治语句 如果任何一行都不会影响其他行,称每一行是自治的。可对其进行重新排序甚至移除任何行二不影响解释其他行。
格式解析策略 相同格式使用空白符解析 由于文本格式固定 ,可以使用使用空白符作为分隔符,将第二个元素提取为积分
1 2 3 score 300 for 3 nights at Bree score 200 for 2 nights at Dol Amroth score 150 for 2 nights at Orthanc
不同格式条件表达式检查解析 以下是文本格式不同的一种场景
1 2 3 4 border grey headline "Musical Cambridge" filter by date in this week show concerts in Cambridge
其每一行都是自治的,但需要不同的处理方式。可以通过条件表达式检查每一行种类,并做处理
1 2 3 4 5 if (isBorder ()) parseBorder ();else if (isHeadline ()) parseHeadline ();else if (isFilter ()) parseFilter ();else if (isShow ()) parseShow ();else throw new RecognitionException (input);
混合格式解析 1 2 3 4 5 300 for stay 3 nights at Bree 150 per day for stay 2 nights at Bree 50 for spa treatment at Dol Amroth 60 for stay 1 night at Orthanc or Helm 's Deep or Dunharrow 1 per dollar for dinner at Bree
可以通过一个顶级的处理器识别出 3 个子句,通过for和at关键字拆解出以下子句
然后采用不同格式的解析模式,对子句进行解析
使用时机
通常只有面对简单的自治语句或者只有一个嵌套上下文时,才会用分隔符制导翻译。
自治语句语法分析示例 DSL 一家连锁酒店的奖励规则,DSL 如下表达:
1 2 3 4 5 300 for stay 3 nights at Bree 150 per day for stay 2 nights at Bree 50 for spa treatment at Dol Amroth 60 for stay 1 night at Orthanc or Helm 's Deep or Dunharrow 1 per dollar for dinner at Bree
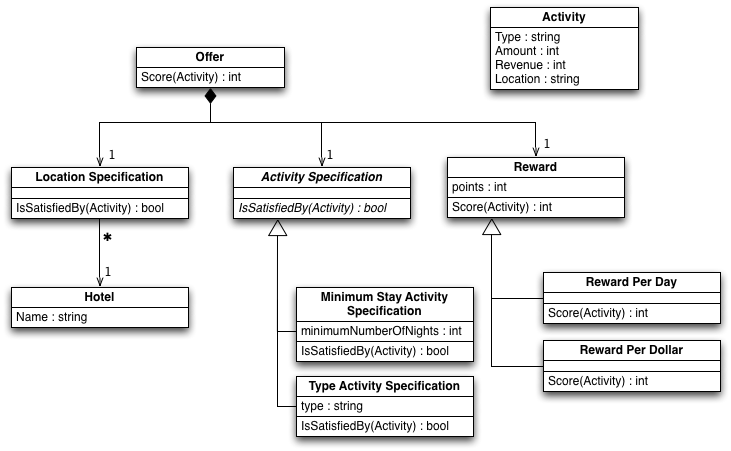
语义模型 类图 模型解释
Location Specification:检查发生地址是否符合奖励规则
Activity Specification:检查活动是否符合奖励规则
Reward:负责计算积分
Offer:负责对业务流程的封装,我们的目标就是将行语句解析成一个 Offer 对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Offer { public int Score (Activity a) { return Location.IsSatisfiedBy(a) && Activity.IsSatisfiedBy(a) ? Reward.Score(a):0 ; } public Reward Reward { get; set; } public LocationSpecification Location { get; set; } public ActivitySpecification Activity { get; set; } }
模型逻辑实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 class Activity { public string Type { get ; set ; } public int Amount { get ; set ; } public int Revenue { get ; set ; } public string Location { get ; set ; } } class LocationSpecification { private readonly IList<Hotel> hotels = new List<Hotel>(); public LocationSpecification (params String[] names foreach (string n in names) hotels.Add(Repository.HotelNamed(n)); } public bool IsSatisfiedBy (Activity a ) Hotel hotel = Repository.HotelNamed(a.Location); return hotels.Contains(hotel); } } abstract class ActivitySpecification { public abstract bool isSatisfiedBy (Activity a ) } class MinimumNightStayActivitySpec : ActivitySpecification { private readonly int minimumNumberOfNights; public MinimumNightStayActivitySpec (int numberOfNights this .minimumNumberOfNights = numberOfNights; } public override bool isSatisfiedBy (Activity a ) return a.Type == "stay" ? a.Amount >= minimumNumberOfNights : false ; } } class TypeActivitySpec : ActivitySpecification { private readonly string type; public TypeActivitySpec (string type this .type = type; } public override bool isSatisfiedBy (Activity a ) return a.Type == type; } } class Reward { protected int points; public Reward (int pointsthis .points = points; } virtual public int Score (Activity activity ) return points; } } class RewardPerDay : Reward { public RewardPerDay (int pointsbase (points ) public override int Score (Activity activity ) if (activity.Type != "stay" ) throw new ArgumentException("can only use per day scores on stays" ); return activity.Amount * points; } } class RewardPerDollar : Reward { public RewardPerDollar (int pointsbase (points ) public override int Score (Activity activity ) return activity.Revenue * points; } }
语法分析器
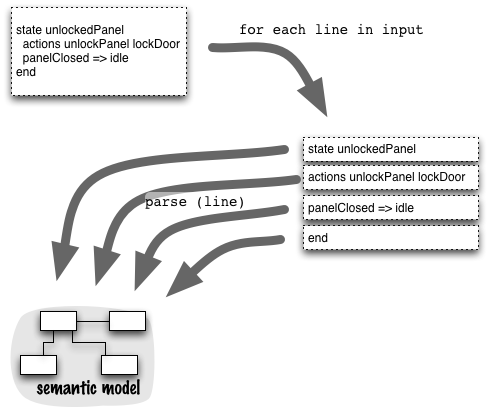
读取每一行输入并处理,使用”&”作为续行符解析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class OfferScriptParser { readonly TextReader input; readonly List<Offer> result = new List<Offer>(); public OfferScriptParser (TextReader input ) this .input = input; } public List<Offer> Run () string line; while ((line = input.ReadLine()) != null ) { line = appendContinuingLine(line); parseLine(line); } return result; } private string appendContinuingLine (string line if (IsContinuingLine(line)) { var first = Regex.Replace(line, @"&\s*$" , "" ); var next = input.ReadLine(); if (null == next) throw new RecognitionException(line); return first.Trim() + " " + appendContinuingLine(next); } else return line.Trim(); } private bool IsContinuingLine (string line return Regex.IsMatch(line, @"&\s*$" ); }
对行进行预处理,去除注释并忽略空行,因为行解析行为足够复杂,所以之后将行解析工作委托给 OfferLineParser 对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class OfferScriptParser { private void parseLine (string line line = removeComment(line); if (IsEmpty(line)) return ; result.Add(new OfferLineParser().Parse(line.Trim())); } private bool IsEmpty (string line return Regex.IsMatch(line, @"^\s*$" ); } private string removeComment (string line return Regex.Replace(line, @"#.*" , "" ); } }
将行分解成子句,然后对每个子句调用各自语法分析方法。
这里使用正则表达式将行解析成 3 个子句,并对子句再进行各自解析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class OfferLineParser { public Offer Parse (string line var result = new Offer(); const string rewardRegexp = @"(?<reward>.*)" ; const string activityRegexp = @"(?<activity>.*)" ; const string locationRegexp = @"(?<location>.*)" ; var source = rewardRegexp + keywordToken("for" ) + activityRegexp + keywordToken("at" ) + locationRegexp; var m = new Regex(source).Match(line); if (!m.Success) throw new RecognitionException(line); result.Reward = parseReward(m.Groups["reward" ].Value); result.Location = parseLocation(m.Groups["location" ].Value); result.Activity = parseActivity(m.Groups["activity" ].Value); return result; } private String keywordToken (String keyword ) return @"\s+" + keyword + @"\s+" ; } }
子句解析
解析过程可以看到正则表达式解析是非常重要的一部分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class OfferLineParser { private LocationSpecification parseLocation (string input if (Regex.IsMatch(input, @"\bor\b" )) return parseMultipleHotels(input); else return new LocationSpecification(input); } private LocationSpecification parseMultipleHotels (string input String[] hotelNames = Regex.Split(input, @"\s+or\s+" ); return new LocationSpecification(hotelNames); } private ActivitySpecification parseActivity (string input if (input.StartsWith("stay" )) return parseStayActivity(input); else return new TypeActivitySpec(input); } private ActivitySpecification parseStayActivity (string input const string stayKeyword = @"^stay\s+" ; const string nightsKeyword = @"\s+nights?$" ; const string amount = @"(?<amount>\d+)" ; const string source = stayKeyword + amount + nightsKeyword; var m = Regex.Match(input, source); if (!m.Success) throw new RecognitionException(input); return new MinimumNightStayActivitySpec(Int32.Parse(m.Groups["amount" ].Value)); } private Reward parseReward (string input if (Regex.IsMatch(input, @"^\d+$" )) return new Reward(Int32.Parse(input)); else if (Regex.IsMatch(input, @"^\d+ per day$" )) return new RewardPerDay(Int32.Parse(extractDigits(input))); else if (Regex.IsMatch(input, @"^\d+ per dollar$" )) return new RewardPerDollar(Int32.Parse(extractDigits(input))); else throw new RecognitionException(input); } private string extractDigits (string input return Regex.Match(input, @"^\d+" ).Value; } }
非自治语句语法分析示例 DSL 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 events doorClosed D1CL drawerOpened D2OP lightOn L1ON doorOpened D1OP panelClosed PNCL end resetEvents doorOpened end commands unlockPanel PNUL lockPanel PNLK lockDoor D1LK unlockDoor D1UL end state idle actions unlockDoor lockPanel doorClosed => active end state active drawerOpened => waitingForLight lightOn => waitingForDrawer end state waitingForLight lightOn => unlockedPanel end state waitingForDrawer drawerOpened => unlockedPanel end state unlockedPanel actions unlockPanel lockDoor panelClosed => idle end
语法解析器
loadFile 方法载入文件
run 方法对文件进行逐行解析
使用 LineParser 行语法分析器进行解析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class StateMachineParser { public static StateMachine loadFile (String fileName ) try { StateMachineParser loader = new StateMachineParser(new FileReader(fileName)); loader.run(); return loader.machine; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public StateMachineParser (Reader reader ) input = new BufferedReader(reader); } private final BufferedReader input; void run () String line; setLineParser(new TopLevelLineParser(this )); try { while ((line = input.readLine()) != null ) lineParser.parse(line); input.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finishMachine(); } private LineParser lineParser; void setLineParser (LineParser lineParser ) this .lineParser = lineParser; } }
行语法分析器
LineParser 对 parse 方法进行了封装
TopLevelLineParser 子类只需要实现 doParse 即可,负责顶级条件语句的解析,只查找命令开始的块
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 abstract class LineParser { protected final StateMachineParser context; protected LineParser (StateMachineParser context ) this .context = context; } void parse (String s ) line = s; line = removeComment(line); line = line.trim(); if (isBlankLine()) return ; doParse(); } protected String line; private boolean isBlankLine () return line.matches("^\\s*$" ); } private String removeComment (String line ) return line.replaceFirst("#.*" , "" ); } abstract void doParse () } class TopLevelLineParser extends LineParser { TopLevelLineParser(StateMachineParser parser) { super(parser); } void doParse () if (hasOnlyWord("commands" )) context.setLineParser(new CommandLineParser(context)); else if (hasOnlyWord("events" )) context.setLineParser(new EventLineParser(context)); else if (hasOnlyWord("resetEvents" )) context.setLineParser(new ResetEventLineParser(context)); else if (hasKeyword("state" )) processState(); else failToRecognizeLine(); } protected boolean hasOnlyWord (String word ) if (words(0 ).equals (word)) { if (words().length != 1 ) failToRecognizeLine(); return true ; } else return false ; } protected boolean hasKeyword (String keyword ) return keyword.equals (words(0 )); } protected String[] words () return line.split("\\s+" ); } protected String words (int index return words()[index]; } protected void failToRecognizeLine () throw new RecognitionException(line); } }
命令行子句解析
以 end 为结束语句
end 之间行语句进行解析注册
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class CommandLineParser { void doParse () if (hasOnlyWord("end" )) returnToTopLevel(); else if (words().length == 2 ) context.registerCommand(new Command(words(0 ), words(1 ))); else failToRecognizeLine(); } } class LineParser { protected void returnToTopLevel () context.setLineParser(new TopLevelLineParser(context)); } } class StateMachineParser { void registerCommand (Command c ) commands.put(c.getName(), c); } private Map<String, Command> commands = new HashMap<String, Command>(); Command getCommand (String word ) { return commands.get (word); } }
状态行子句解析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class TopLevelLineParser { private void processState () State state = context.obtainState(words(1 )); context.primeMachine(state); context.setLineParser(new StateLineParser(context, state)); } } class StateMachineParser { State obtainState (String name ) { if (!states.containsKey(name)) states.put(name, new State(name)); return states.get (name); } void primeMachine (State state ) if (machine == null ) machine = new StateMachine(state); } private StateMachine machine; } class StateLineParser { void doParse () if (hasOnlyWord("end" )) returnToTopLevel(); else if (isTransition()) processTransition(); else if (hasKeyword("actions" )) processActions(); else failToRecognizeLine(); } private boolean isTransition () return line.matches(".*=>.*" ); } private void processTransition () String[] tokens = line.split("=>" ); Event trigger = context.getEvent(tokens[0 ].trim()); State target = context.obtainState(tokens[1 ].trim()); state.addTransition(trigger, target); } private void processActions () for (String s : wordsStartingWith(1 )) state.addAction(context.getCommand(s)); } }